China recently announced strict new regulations on rare earths, essential for the manufacturing of electric vehicles and other advanced technologies. These regulations aim to protect national security by controlling the production, sale and export of these critical materials. This article explores the potential impact of these measures on global industry, particularly in the context of the energy transition.
Context of the new regulations
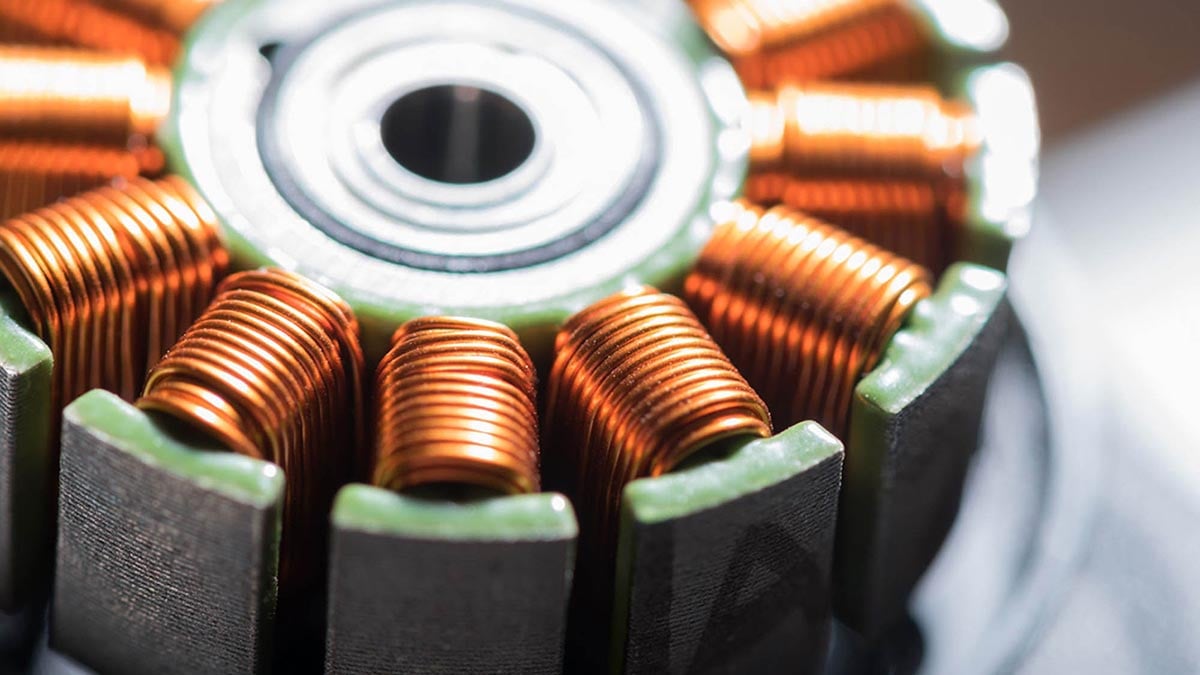
Rare earths are a group of 17 chemical elements essential to many modern technologies. China dominates global production of rare earths, accounting for almost 90% of global production. To secure its supplies and control the industry, China has put in place new regulations which will come into force on October 1, 2024. These measures impose a rigorous traceability system and restrict exports for reasons of national security.
| Element | Main use |
|---|---|
| Neodymium | Magnets for electric motors and wind generators |
| Dysprosium | Strengthening magnets for high temperatures |
| Terbium | Used in displays and fluorescent lighting |
Impact on the automotive industry
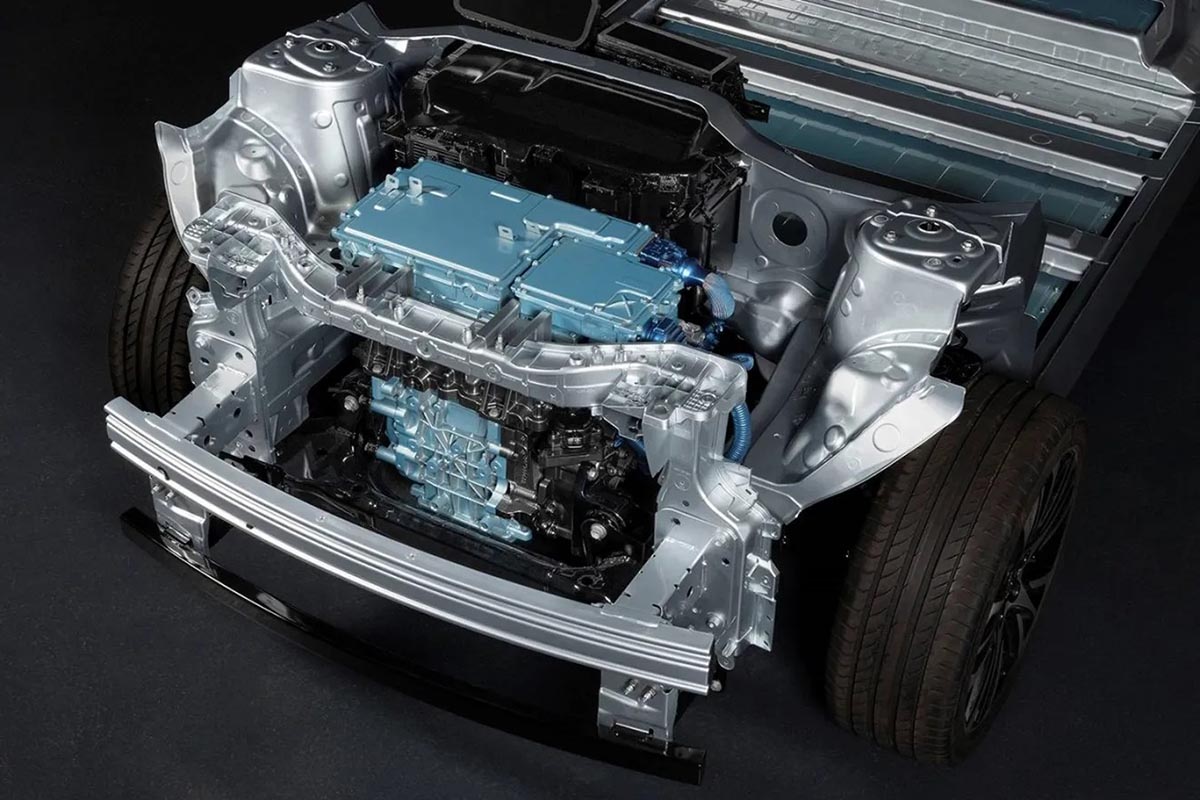
Rare earths are crucial for the production of electric vehicles, particularly for permanent magnets in electric motors. These motors, used by many manufacturers, contain around 30% rare earths, mainly neodymium. Restrictions on the export of these materials could disrupt the global supply chain and increase production costs for electric vehicles.
Implications for electric vehicles:
- Increased dependence : Manufacturers will have to find alternative sources or develop technologies less dependent on rare earths.
- Increased costs : Restrictions could lead to higher prices for electric vehicles.
- Research and development : Encouragement to invest in innovative solutions to reduce the use of rare earths.
International response
The European Union (EU) and the United States are closely monitoring these developments. The EU has already set ambitious targets to increase domestic production of rare earths and other critical materials by 2030. New Chinese regulations could accelerate these efforts, pushing Western countries to strengthen their production capacities and diversify their sources supply.
Response strategies :
- Diversification of sources : Investments in the exploration of rare earth deposits outside China.
- Alternative technologies : Development of electric motors without permanent magnets.
- International cooperation : Partnerships to secure supply chains and reduce dependence on China.
Challenges and opportunities
The implementation of new Chinese regulations on rare earths presents both challenges and opportunities for the global industry. On the one hand, restrictions could disrupt supply chains and increase production costs. On the other, they could stimulate innovation and research into alternative technologies, thereby reducing dependence on rare earths in the long term.
| Appearance | Detail |
|---|---|
| Challenges | Disruption of supply chains, rising costs |
| Opportunities | Technological innovation, diversification of supply sources |
China’s new regulations on rare earths represent a major turning point for the global technology and energy industry. As China seeks to secure its strategic resources, Western countries will need to adapt their strategies to ensure a stable supply of critical materials. This could accelerate the transition to more sustainable technologies that are less dependent on scarce resources, while strengthening the resilience of global supply chains.